What are the key considerations in delegation of authority in an organizational situation and what are the essential pre-requisites required for the purpose.
What are the key considerations in delegation of authority in an organizational situation and what are the essential pre-requisites required for the purpose. Explain with few examples from the organization to you. Briefly describe the basic details of the organization you are referring to.
A manager alone cannot perform all the tasks assigned to him. In order to meet the targets, the manager should delegate authority. Delegation of Authority means division of authority and powers downwards to the subordinate. Delegation is about entrusting someone else to do parts of your job. Delegation of authority can be defined as subdivision and sub-allocation of powers to the subordinates in order to achieve effective results.
Delegation of authority is one vital organizational process. It is inevitable along with the expansion and growth of a business enterprise. Delegation means assigning of certain responsibilities along with the necessary authority by a superior to his subordinate managers. Delegation does not mean surrender of authority by the higher level manager. It only means transfer of certain responsibilities to subordinates and giving them the necessary authority, which is necessary to discharge the responsibility properly. Delegation is quite common in all aspects of life including business. Even in the college, the principal delegates some of his authority to the vice-principal.
Elements of Delegation
1. Authority - in context of a business organization, authority can be defined as the power and right of a person to use and allocate the resources efficiently, to take decisions and to give orders so as to achieve the organizational objectives. Authority must be well- defined. All people who have the authority should know what is the scope of their authority is and they shouldn’t misutilize it. Authority is the right to give commands, orders and get the things done. The top level management has greatest authority. Authority always flows from top to bottom. It explains how a superior gets work done from his subordinate by clearly explaining what is expected of him and how he should go about it. Authority should be accompanied with an equal amount of responsibility. Delegating the authority to someone else doesn’t imply escaping from accountability. Accountability still rest with the person having the utmost authority.
2. Responsibility - is the duty of the person to complete the task assigned to him. A person who is given the responsibility should ensure that he accomplishes the tasks assigned to him. If the tasks for which he was held responsible are not completed, then he should not give explanations or excuses. Responsibility without adequate authority leads to discontent and dissatisfaction among the person. Responsibility flows from bottom to top. The middle level and lower level management holds more responsibility. The person held responsible for a job is answerable for it. If he performs the tasks assigned as expected, he is bound for praises. While if he doesn’t accomplish tasks assigned as expected, then also he is answerable for that.
3. Accountability - means giving explanations for any variance in the actual performance from the expectations set. Accountability can not be delegated. For example, if ’A’ is given a task with sufficient authority, and ’A’ delegates this task to B and asks him to ensure that task is done well, responsibility rest with ’B’, but accountability still rest with ’A’. The top level management is most accountable. Being accountable means being innovative as the person will think beyond his scope of job. Accountability, in short, means being answerable for the end result. Accountability can’t be escaped. It arises from responsibility.
For achieving delegation, a manager has to work in a system and has to perform following steps :
1. Assignment of tasks and duties
2. Granting of authority
3. Creating responsibility and accountability
Delegation of authority is the base of superior-subordinate relationship, it involves following steps:-
1. Assignment of Duties - The delegator first tries to define the task and duties to the subordinate. He also has to define the result expected from the subordinates. Clarity of duty as well as result expected has to be the first step in delegation.
2. Granting of authority - Subdivision of authority takes place when a superior divides and shares his authority with the subordinate. It is for this reason; every subordinate should be given enough independence to carry the task given to him by his superiors. The managers at all levels delegate authority and power which is attached to their job positions. The subdivision of powers is very important to get effective results.
3. Creating Responsibility and Accountability - The delegation process does not end once powers are granted to the subordinates. They at the same time have to be obligatory towards the duties assigned to them. Responsibility is said to be the factor or obligation of an individual to carry out his duties in best of his ability as per the directions of superior. Responsibility is very important. Therefore, it is that which gives effectiveness to authority. At the same time, responsibility is absolute and cannot be shifted. Accountability, on the others hand, is the obligation of the individual to carry out his duties as per the standards of performance. Therefore, it is said that authority is delegated, responsibility is created and accountability is imposed. Accountability arises out of responsibility and responsibility arises out of authority. Therefore, it becomes important that with every authority position an equal and opposite responsibility should be attached.
Therefore every manager, i.e., the delegator has to follow a system to finish up the delegation process. Equally important is the delegate’s role which means his responsibility and accountability is attached with the authority over to here.
Objectives of Delegation of Authority
1. To reduce the excessive burden on the superiors i.e., executives and managersfunctioning at different levels.
2. To provide opportunities of growth and self development to junior executives.
3. To create a team of experienced and matured managers for the Organisation. Itacts as a technique of management and human resource development.
4. To improve individual as well as overall efficiency of the Organisation.
Process of Delegation of Authority at American Express
It is an assortment of such experiences that, for over a thousand employees at Amex India, make the company a great place to work. This is reflected in the long tenures that employees have at Amex. There are many factors that influence employees' decision to stay in a job market or create jobs by turning entrepreneurs. Working for large corporations has its own advantages. Apart from the assurance and security of a good salary every month end, there is also a pride attached to working in reputed companies. In the financial services sector, Amex, which has over a thousand employees in India, its largest employee base anywhere outside the US, presents a good opportunity. The company also scores high on employee freedom at work front.
The hallmark of any good corporate is the extent of decentralisation of power and authority. "At Amex, we have a four-stage development plan that employees get to create.
When employees set their own goals, they are more likely to achieve it," says Rai, talking
about the company's four-stage development plan that employees help make, getting a greater say in shaping company policy and direction.
about the company's four-stage development plan that employees help make, getting a greater say in shaping company policy and direction.
At Amex, individual leadership is given to junior managers, executional leadership rests with middle managers and strategic leadership roles are vested with vice presidents. Visionary leadership functions rest with the global heads. So the company has a clear function and well distributed authority at all levels. "Such clear distribution eliminates the need for much supervision, management of day to day employee affairs and also guarantees employee freedom," adds Rai.
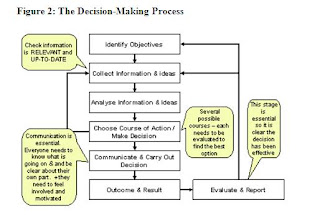
Delegation process involves four distinct stages. The process of delegation moves
through these stages. The following figure shows the stages in the process of delegation
of authority.
through these stages. The following figure shows the stages in the process of delegation
of authority.
Advantages / Importance of Delegation of Authority
1. Relieves manager for more challenging jobs: Delegation makes it possible for the managers to distribute their workload to others. Thus, managers are relieved of routine work and they can concentrate on higher functions of management like planning, organising, controlling, etc.
2. Leads to motivation of subordinates: Subordinates are encouraged to give their best at work when they have authority with responsibility. They take more initiative and interest in the work and are also careful and cautious in their work. Delegation leads to motivation of employees and manpower development.
3. Facilitates efficiency and quick actions: Delegation saves time enabling tile subordinates to deal with the problems promptly. They can take the decisions quickly within their authority. It is not necessary to go to the superiors for routine matters. This raises the overall efficiency in an Organisation and offers better results in terms of production, turnover and profit.
4. Improves employee morale: Delegation raises the morale of subordinates as they are given duties and supporting authority. They feel that they are responsible
employees. The attitude and outlook of subordinates towards work assigned becomes more constructive.
employees. The attitude and outlook of subordinates towards work assigned becomes more constructive.
5. Develops team spirit: Due to delegation, effective communication develops between the superiors and subordinates. The subordinates are answerable to superiors and the superiors are responsible for the performance of subordinates. This brings better relations and team spirit among the superiors and subordinates
6. Maintains cordial relationships: The superiors trust subordinates and give them necessary authority. The subordinates accept their accountability and this develops cordial superior-subordinate relationships.
7. Facilitates management development: Delegation acts as a training ground for management development. It gives opportunity to subordinates to learn, to grow and to develop new qualities and skills. It builds up a reservoir of executives, which can be used as and when required. Delegation creates managers and not mere messengers.